Why do we need a Customer Journey Map?
A customer journey map visualizes the customer journey from the perspective of potential customers. The most important touchpoints and the associated interactions, actions and emotions are mapped from the customer’s point of view. In this way, companies can always be close to their clientele and respond quickly to customer needs. The customer journey map therefore helps you to track the customer experience, uncover gaps in the process and optimize the customer experience.
Important: Clearly define in advance whether your customer journey map should depict the status quo or the desired target experience. Both are possible, but will produce different results. A map that shows the current state is particularly useful when it comes to revealing any sticking points. The Future State Map, on the other hand, starts with the elimination of these sticking points.
It is advisable to create one map for the current state and one for the target state of the customer experience. These can then be compared to determine which experiences customers are currently having and how these should ideally change.
Create your Customer Journey in 6 steps
The following 6 steps should be followed when creating your Customer Journey Map:
- Research and collect data
- Define personas
- List touchpoints and individual steps and put them in a chronological order
- Include emotions
- Create a Customer Journey Map
- Take action – analyze, optimize and start from scratch
1. Research and collect data
In order to understand the customer journey and the experience as realistically as possible, the first step is to collect as much data as possible. Both internal and external sources can be used for this purpose. The most obvious way to do this is to track user behavior (e.g., via Google Analytics, social media monitoring, or email marketing statistics). However, valuable data is also generated when you interview customers directly. This gives you even deeper insights into the emotional world and thoughts of customers. It is important to consider data from both quantitative and qualitative evaluations and to compare them with each other. Often, certain theses can be derived from surveys, which can then be evaluated with the help of Google Analytics, for example.
2. Define personas
Personas are a central component of your customer journey. They are fictitious people who are representative of an entire target group. Their main purpose is to help you put yourself in the customer’s shoes and see things from their perspective. In addition to classic sociodemographic characteristics such as gender, age, marital status, etc., great attention should also be paid to values, goals and pain points.
To make your persona as close and real as possible, it is best to give it a face and a name.
The data collected in the previous step should be used to create the personas. Your existing customer base is particularly informative here.
3. List touchpoints and individual steps and put them in a time sequence
The next step is to record every experience that this persona has with your brand/company in the broadest sense. This involves listing touchpoints, both online and offline, as well as channels, but also steps, i.e. experiences per se. To do this, it’s best to divide the buying process into phases and walk through it, phase by phase, in the customer’s shoes.
Touchpoints and steps are often understood to be synonymous. However, touchpoints refer to specific interactions between the persona and the company or brand. Steps, on the other hand, refer to any experience. For example, the persona may identify a personal need without having already encountered a product as a possible solution. Thus, no interaction with the brand has taken place yet.
In this step, it is also a good idea to consider whether important touchpoints are still missing or whether there are superfluous ones that can be eliminated.

4. Include emotions
Once all the relevant touchpoints, channels and steps are known, the journey can now be played out with the persona’s hat on his head. Always consider how the persona feels in the respective situation, whether he or she reaches his or her goal, encounters obstacles, or also whether he or she has pleasant experiences.
To visualize the emotional world, it is a good idea to rank emotions on a scale ranging, for example, from +2 (very positive) to -2 (very negative).
Touchpoints or steps that trigger negative emotions should be modified if possible or even removed altogether. Admittedly, not every experience can and must be fully positive. However, a neutral impression should at least always be strived for.
5. Create Customer Journey Map
Now it is necessary to clearly present the information developed in the previous steps. The map can be created on paper or electronically, as desired. There is no right or wrong way to do this, because each map is just as individual as the journey itself. However, there are some proven patterns. For example, the map is easiest to follow if it is divided into the various phases of the journey. How these phases are named is again very individual. In principle, however, a journey always follows the following stages: Before the purchase (awareness phase), during the purchase (purchase), and after the purchase (post-purchase).
Options for representing the customer journey map:
- Linear models: They are the simplest way to represent the customer journey and stringently follow the different phases of the customer journey. Although this makes them very clear, they are also often highly simplified.
- Table: This form enables the inclusion of a wide variety of comprehensive information, but is significantly less clear than linear models.
- Marketing Funnel: Alternatively, the customer journey can also be based on the marketing funnel. In this case, the journey takes on a funnel or hourglass shape.
- «Day in the Life» model: A typical day in the life of a potential customer is outlined here. This model is particularly suitable for everyday products or impulse purchases. On the other hand, it makes little sense for high-priced offers that are based on a long consideration process.
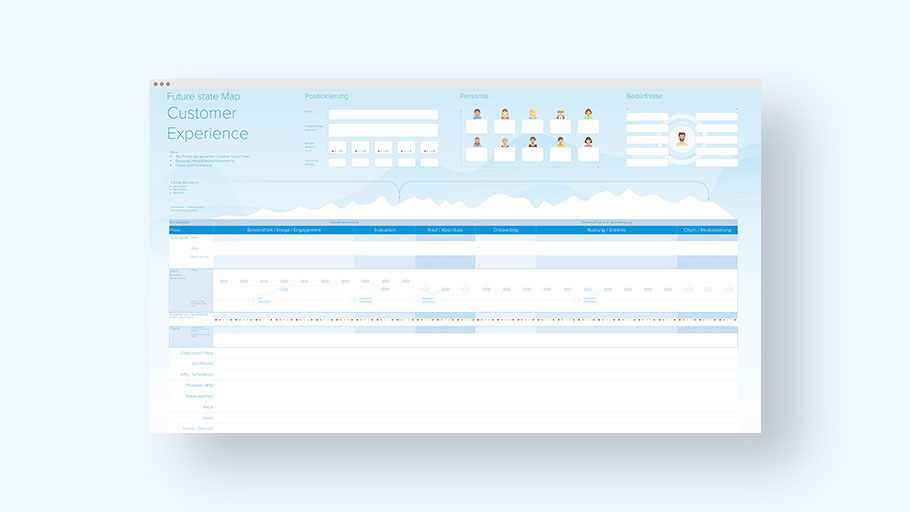
Free template for optimizing the customer experience
Looking for an easy-to-use template to help you visualize and optimize your company’s customer experience?
Our template offers you a simple way to display the steps and touchpoints of your customers at a glance and identify optimization potential.
6. Take action – analyze, optimize and start from scratch
Once the map has been created, it must be used. With its help, it can be determined whether and where touchpoints can be optimized, newly integrated or completely eliminated. Integrating new touchpoints can be worthwhile, but they must also be adequately and regularly managed. Otherwise, this can have a negative impact on customer satisfaction.
However, it must never be forgotten that the customer journey map is only a model which attempts to approximate the actual purchasing process as closely as possible. To what extent the assumptions are correct and the measures taken actually have an effect remains to be seen in practice. In order to ensure that the needs and expectations of customers are met, it is therefore important to continuously review measures and make adjustments where necessary.
Advantages of creating a Customer Journey Map
- Improved customer experience, which in turn leads to more conversion and an increase in revenue.
- Enables differentiation to be created through the experience.
- Helps to better understand decisions made by your own clientele and thus be able to act more empathetically towards them.
- Shows what resources are being used to build the customer experience.
- Identifies weaknesses and gaps in processes.
- Helps create an effective and cohesive customer experience where strategic decisions and projects can be aligned.
- Helps UX designers put the customer experience in context.
- Helps teams understand the customer experience from different perspectives and promotes alignment between different teams.
Tips for creating a customer journey map
- Extensive data collection and analysis forms the basis for making the process as realistic and objective as possible. If data is missing, assumptions may be made, but they should always be marked as such.
- The rule is: a separate customer journey for each persona.
- For a comprehensive view, customer journey mapping should not be carried out by just one department, but all departments should be included in the process.
- The customer experience is subject to constant optimization. It should not be seen as a project that has a starting point and an end point.
- At the beginning, clearly define whether the map should depict the status quo or the target experience.
- In the B2B area, the end user should always be included.
Beispiele für schlechte Customer Experience
Zeigt das vollständige Bild der Kundenerfahrung mit der Marke über mehrere Kanäle.
Zeigt das vollständige Bild der Kundenerfahrung mit der Marke über mehrere Kanäle.
Allgemeine Kundenerfahrung
Verstehen des großen Ganzen
Beispiele für gute Customer Experience
Produkt-/dienstleistungsbezogen
Spezifischer Kundentyp
Konzentriert sich auf die Erfahrung, die der Kunde bei der Interaktion mit einem bestimmten Produkt/Dienstleistung macht.
Eintauchen in Details
Eignet sich, wenn man weiss, welche Probleme vorliegen und geeignete Lösungen gefunden werden müssen.
Takeaways
The journey of potential customers can be visually prepared using a customer journey map. It helps you to better understand your target group. It also reveals weak points and is a good tool for the continuous optimization of the customer experience. The following steps will help you create your own customer journey quickly and easily:
- Research and collect data
- Define personas
- List touchpoints and individual steps and put them in a chronological order
- Include emotions
- Create a Customer Journey Map
- Take action – analyze, optimize and start from scratch
This map will help you to align your marketing activities in the best possible way with your customers and their needs.
Need help with the CX Map for your business?
This might also interest you
Customer Journey: The 6 Phases
Customer Experience (CX): Definition, strategies and examples
